Price Controls Price Ceiling Or Price Floor Are Quizlet

But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
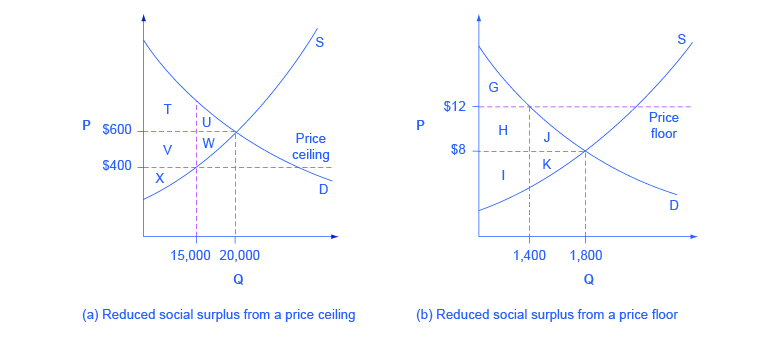
Price controls price ceiling or price floor are quizlet. It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price. A price floor of 10. Consumer surplus under random allocation is the green area. This is the currently selected item.
Taxation and dead weight loss. Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government. A price floor of 6 d. A price ceiling of 6 b.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The effect of government interventions on surplus. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the consequence of a binding price floor. Which of the following price controls would cause a shortage of 20 units of the good.
Price ceilings and price floors. A price ceiling of 10 c. Price controls refer to the figure. Price ceilings which prevent prices from exceeding a certain maximum cause shortages.
Example breaking down tax incidence. A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service while a price floor is the legal minimum price. Suppose that the supply and demand for wheat flour are balanced at the current price and that the government then fixes a lower maximum price. If goods are allocated randomly to buyers with values between 30 and 6 the average value will be 18.
Price and quantity controls. When there is a price control the buyers with the highest valued uses cannot outbid other buyers so goods will flow to any buyer willing to pay more than the controlled price of 6. Price floors which prohibit prices below a certain minimum cause surpluses at least for a time. Price floors and price ceiling price floors.
Start studying price controls. If a price floor is imposed at 15 per unit when the equilibrium market price is 12 there will be. However when a government imposes price controls the eventual consequence can be the creation of excess demand in the case of price ceilings or excess supply in the case of price floors. Price floors are minimum prices set by the government for certain commodities and services that it believes are being sold in an unfair market with too low of a price and thus their producers deserve some assistance.