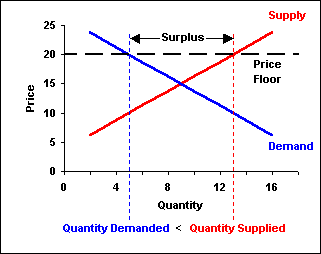
Price Floors And Ceiling Prices Both Cause Shortages
However price ceiling in a long run can cause adverse effect on market and create huge market inefficiencies.
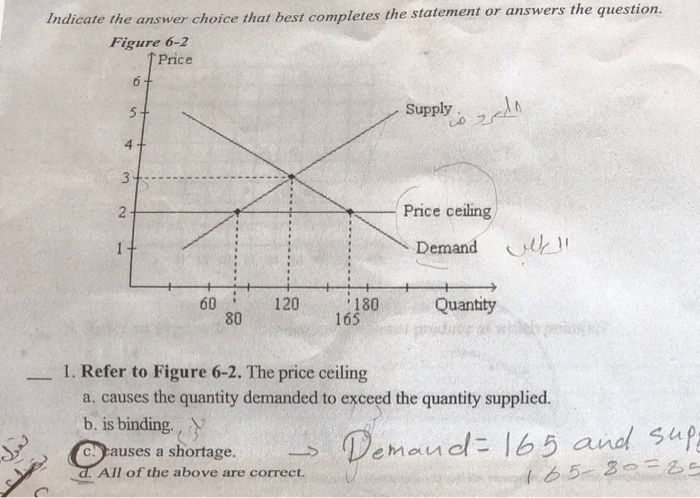
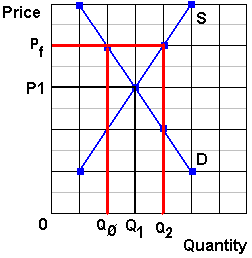
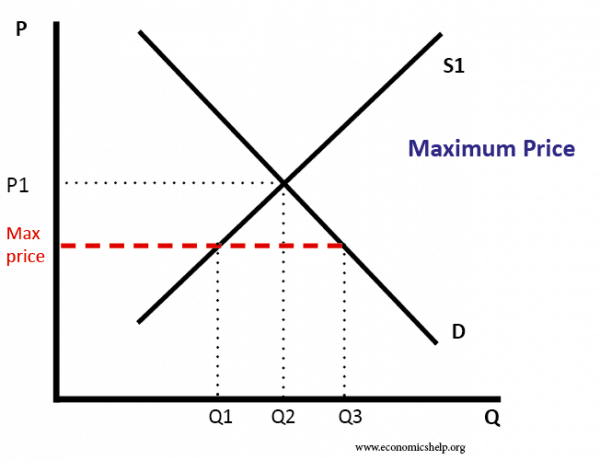
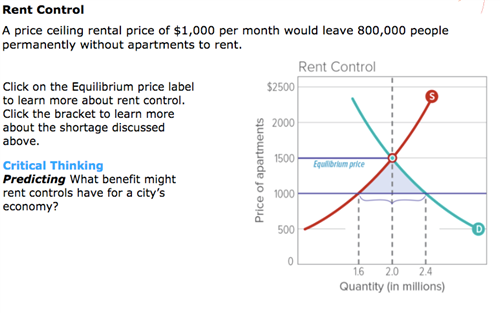
Price floors and ceiling prices both cause shortages. When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result. Percentage tax on hamburgers. Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level. An effective price ceiling will a induce new firms to enter the industry.
Some effects of price ceiling are. Price ceilings and price floors. Price floors and ceiling prices both a interfere with the rationing function of prices b cause the supply and demand curves to shirt until equilibrium is established c cause shortages d cause surpluses. Price ceilings only become a problem when they are set below the market equilibrium price.
When the ceiling is set below the market price there will be excess demand or a supply shortage. Cause the supply and demand curves to shift until equilibrium is established. Interfere with the rationing function of prices. Price and quantity controls.
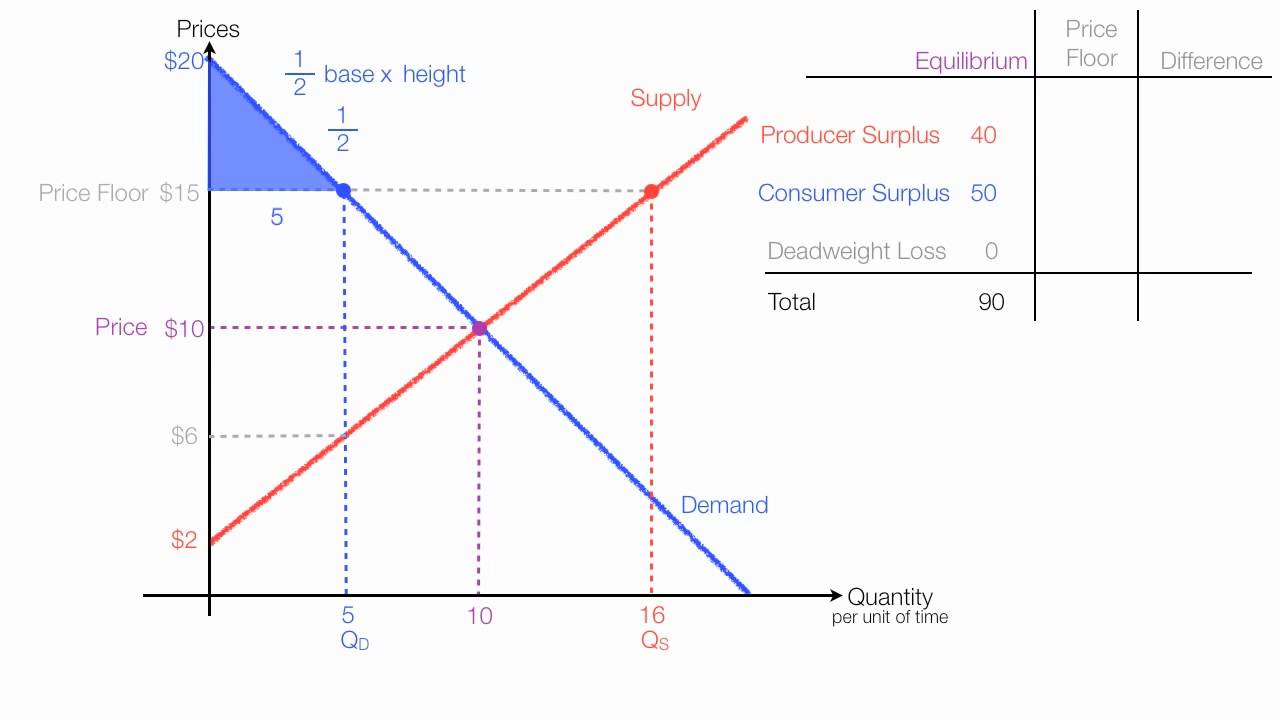
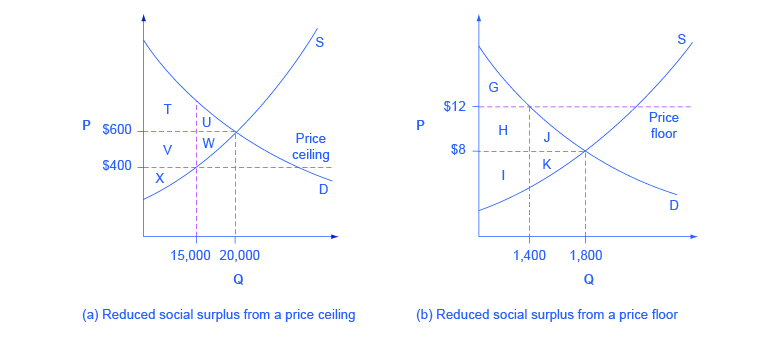
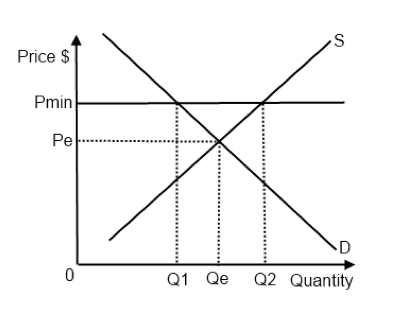
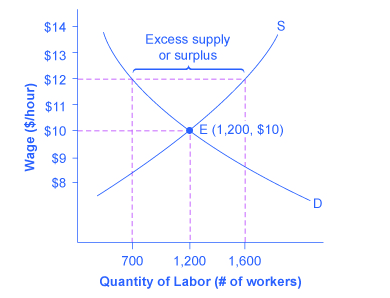
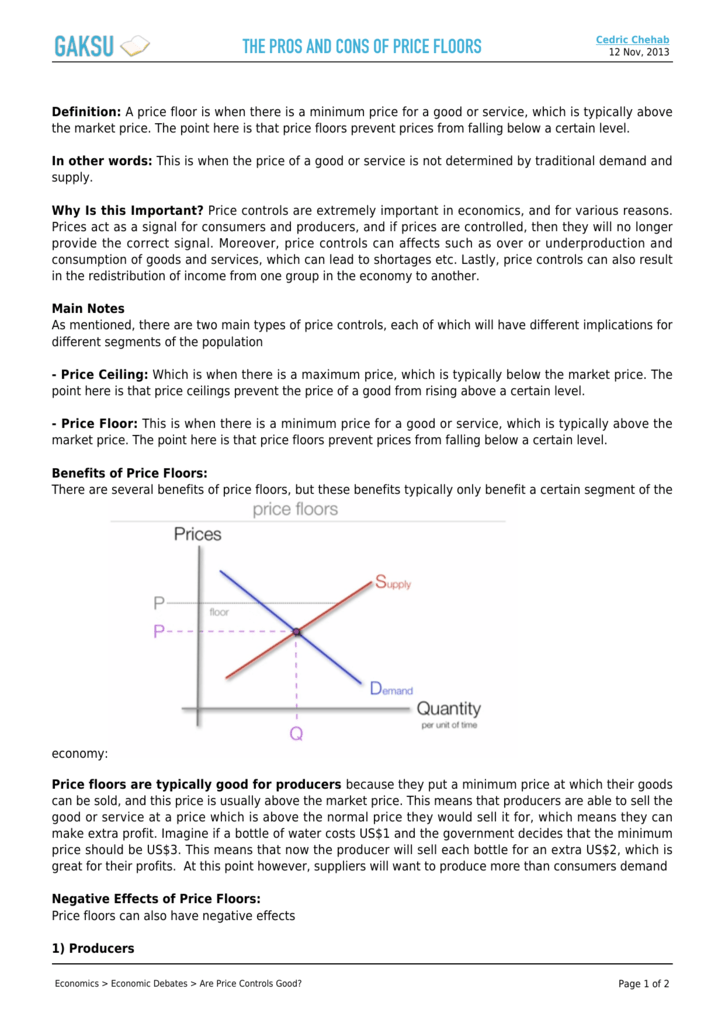
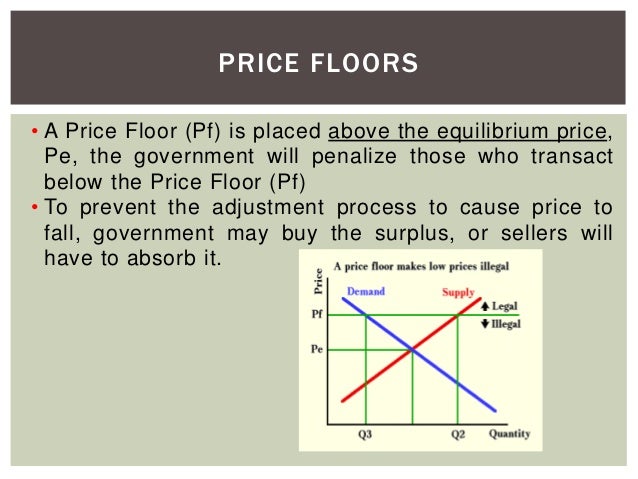
A price floor means that. Producers won t produce as much at the lower price while consumers will demand more because the goods are cheaper. Price floors and ceiling prices. If price ceiling is set above the existing market price there is no direct effect.
Interfere with the rationing function of prices. Price ceilings which prevent prices from exceeding a certain maximum cause shortages. Example breaking down tax incidence. This is the currently selected item.
Suppose that the supply and demand for wheat flour are balanced at the current price and that the government then fixes a lower maximum price. Cause the supply and demand curves to shift until equilibrium is established. But if price ceiling is set below the existing market price the market undergoes problem of shortage. A good example of this is the oil industry where buyers can be victimized by price manipulation.
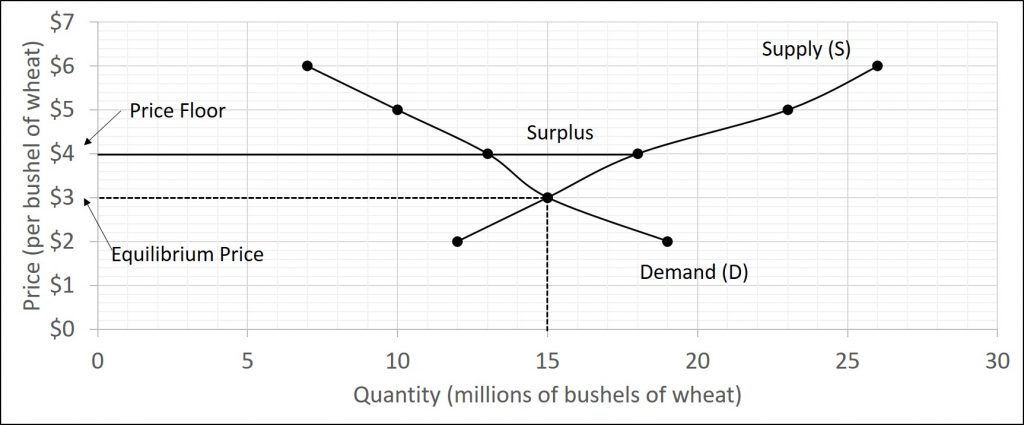
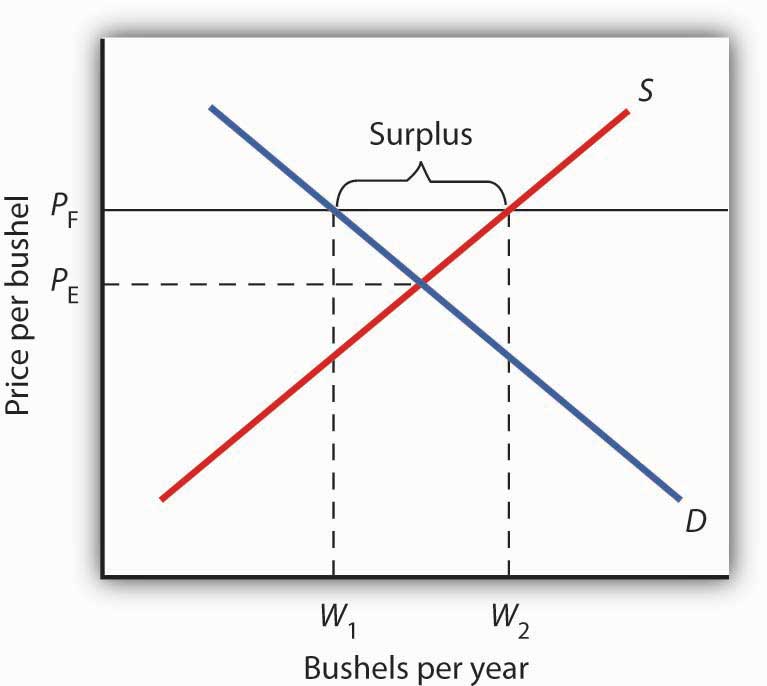
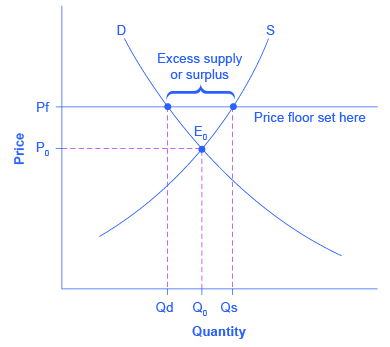
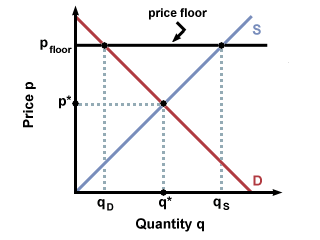
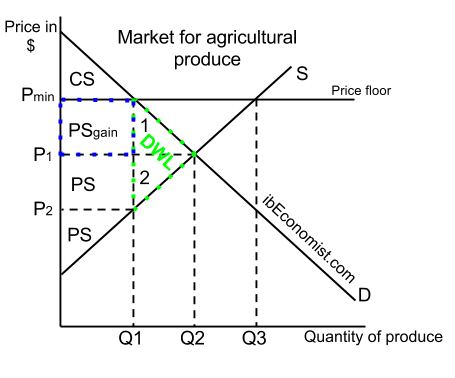
The purpose of a minimum price is to protect producers from receiving low prices for their produce. The graph below illustrates how price floors work. Interfere with the rationing function of prices. Price floors and ceiling prices.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand. Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. They are usually put in place to protect vulnerable buyers or in industries where there are few suppliers. Price ceilings impose a maximum price on certain goods and services.
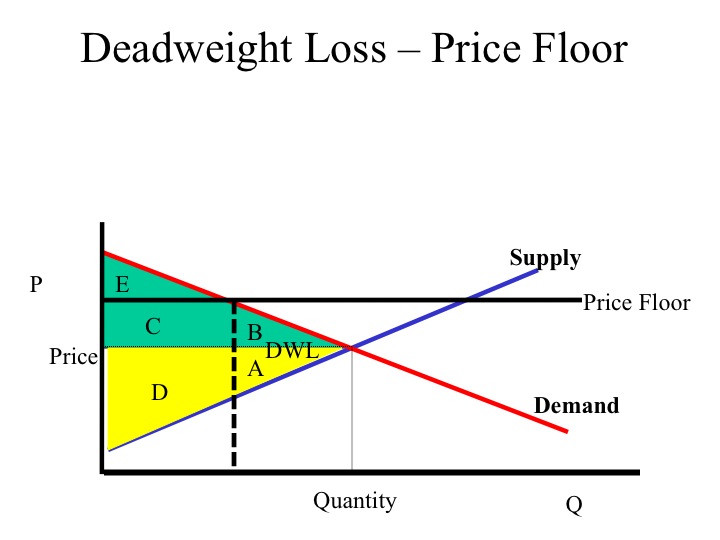
Taxation and dead weight loss. A price floor can cause a surplus while a price ceiling can cause a shortage but not always.

















/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)